Balloon Angioplasty & Stenting
Angioplasty is a procedure performed to open blocked arteries. It is also called PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) or PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). This procedure is performed under local anaesthesia.
Description
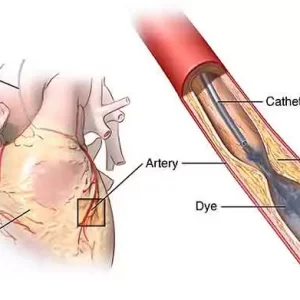
When there is a blocked or a narrowing in an artery, a balloon is inserted into the blockage and then inflated to widen the area of the blockage. A metal cage called a stent may be inserted to hold the blood vessel open once the balloon is retracted. The procedure does not require open surgery and is performed by Cardiologists.
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a procedure performed to open blocked arteries. It is also called PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) or PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention). This procedure is performed under local anaesthesia.
A catheter with a small balloon mounted on the end is passed into the narrowed portion of the coronary artery.
- As the balloon inflates, it pushes the plaque against the wall of the coronary artery. This opens the narrowing and improves the blood flow to the heart muscle.
- The balloon is then deflated and the balloon catheter is removed from the artery.
- In some cases, a tiny wire coil called stent, is inserted with the catheter to support the arterial wall. Stents may not be necessary in some cases.
Coronary Artery Stents
Coronary artery stents are small metallic mesh tubes that are mounted over a balloon catheter and delivered to the narrowed portion of the coronary artery. The balloon is used to expand the stent that presses against the narrowed vessel wall.
Once the balloon has been deflated and withdrawn, the stent stays in place permanently. The inner lining of the artery grows over the surface of the stent incorporating it into the arterial wall permanently. An implanted stent cannot be removed.
2 types Of Stents
- Drug-coated stents (coated)
- Bare-metal stents (uncoated)
Both bare-metal and drug-coated stents have been proven to be safe when used in accordance with their prescribed indications.
In fact, both types of stents have a similar low risk of heart attack and death. You should discuss with your doctor on the choice of stents to be used.